Mealy FSM (Partner B)
FIFO Design (Mealy)
The FIFO buffer is modeled as a Mealy Finite State Machine (FSM) with the following characteristics:
Simplifying Assumptions
- The depth of the FIFO is 2 (it can store at most 2 pieces of data at any point in time).
- Data written on a given cycle cannot also be read on that same cycle.
- Only one piece of data can be read from the FIFO on a given cycle.
FSM Specification
- States:
S0 = 2'b01S1 = 2'b11S2 = 2'b10
- Inputs:
{Write, Read}{0,0}:!write & !read{0,1}:!write & read{1,0}:write & !read{1,1}:write & read
- Outputs:
{Valid, Ready}{0,1}:!valid & ready{1,1}:valid & ready{1,0}:valid & !ready
State Transition Diagram
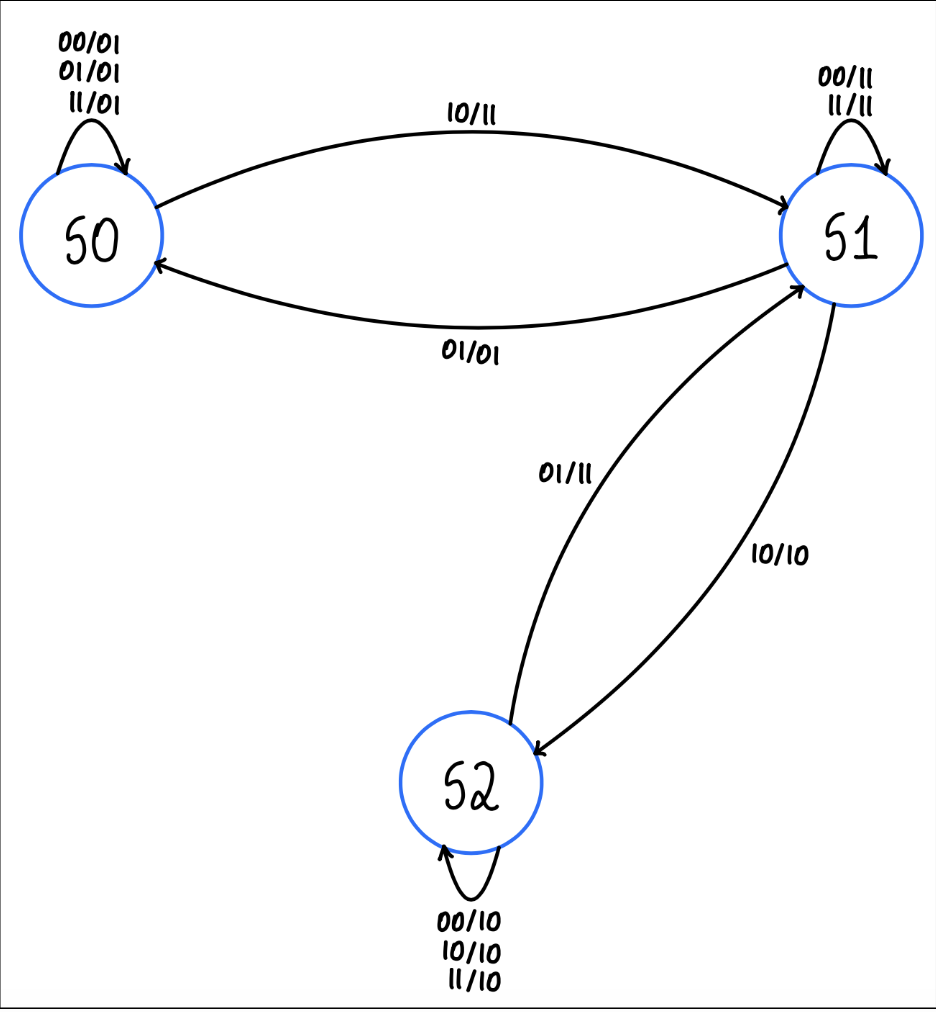
Encoded State Transition Table
| Current State | Input | Next State | Output |
|---|---|---|---|
| {0,1} (S0) | {0,0} (!write & !read) | {0,1} (S0) | {0,1} (!valid & ready) |
| {0,1} (S0) | {0,1} (!write & read) | ||
| {0,1} (S0) | {1,0} (write & !read) | ||
| {0,1} (S0) | {1,1} (write & read) | ||
| {1,1} (S1) | {0,0} (!write & !read) | {1,1} (S1) | {1,1} (valid & ready) |
| {1,1} (S1) | {0,1} (!write & read) | ||
| {1,1} (S1) | {1,0} (write & !read) | ||
| {1,1} (S1) | {1,1} (write & read) | ||
| {1,0} (S2) | {0,0} (!write & !read) | {1,0} (S2) | {1,0} (valid & !ready) |
| {1,0} (S2) | {0,1} (!write & read) | ||
| {1,0} (S2) | {1,0} (write & !read) | ||
| {1,0} (S2) | {1,1} (write & read) |
Instructions
Fill in the blank cells in the above state transition table. This will later help you when you write assertions!
Time to write assertions!
Sample assertions
A couple of sample assertions are filled in below to get you started.
FIFO State Transition Assertion (overlapping implication):
// Empty state transitions
assert property (@(posedge clk) disable iff (rst) (current_state==EMPTY && write && !read) |-> (next_state==PARTIAL) ) else $error("Incorrect empty state transition 1");
Output Assertion (overlapping implication)::
// Empty state output
assert property(@(posedge clk) disable iff (rst)
(current_state==EMPTY) |-> (
(write && !read) ? (valid && ready) : (!valid && ready)
)
) else $error("Incorrect empty output");
Check your understanding
What properties do the sample assertions check for?
Instructions
Given a Verilog implementation of the Mealy FIFO FSM, write a comprehensive set of assertions that verify the state transitions, output, and interface protocol as outlined in the pre-lab document. It may be a good idea to write one assertion per row in the tables above, but you may also be able to write one assertion that covers multiple rows through Boolean logic simplification.
You will write your assertions through the Mealy EDA Playground. Write them at the bottom of design.sv. You can copy over the sample assertions above as a first step. You can click Run to see if your assertions pass. You will need all of your assertions to pass for full credit.
If the EDA Playground is not working, paste the following code into design.sv in EDA Playground. You will write your assertions at the end of this.
// Mealy Implementation
module fifo_fsm (
input logic clk,
input logic rst,
input logic write, // Write request from source
input logic read, // Read request from sink
output logic valid, // Data valid output
output logic ready, // Ready to accept data output
output logic [7:0] data // 8-bit data output
);
// State encoding
typedef enum logic [1:0] {
EMPTY = 2'b01,
PARTIAL = 2'b11,
FULL = 2'b10
} state_t;
state_t current_state, next_state;
// FSM Logic
always_comb begin
next_state = current_state;
case (current_state)
EMPTY: begin
if (write && !read)
next_state = PARTIAL;
else
next_state = EMPTY;
end
PARTIAL: begin
if (write && !read)
next_state = FULL;
else if (!write && read)
next_state = EMPTY;
else
next_state = PARTIAL;
end
FULL: begin
if (!write && read)
next_state = PARTIAL;
else
next_state = FULL;
end
default:
next_state = EMPTY;
endcase
end
// State register
always_ff @(posedge clk) begin
if (rst)
current_state <= EMPTY;
else
current_state <= next_state;
end
// Output logic (Mealy FSM)
always_comb begin
case (current_state)
EMPTY: begin
if (write && !read) begin
valid = 1'b1;
ready = 1'b1;
end else begin
valid = 1'b0;
ready = 1'b1;
end
end
PARTIAL: begin
if (write && !read) begin
valid = 1'b1;
ready = 1'b0;
end else if (!write && read) begin
valid = 1'b0;
ready = 1'b1;
end else begin
valid = 1'b1;
ready = 1'b1;
end
end
FULL: begin
if (!write && read) begin
valid = 1'b1;
ready = 1'b1;
end else begin
valid = 1'b1;
ready = 1'b0;
end
end
default: begin
valid = 1'b0;
ready = 1'b1;
end
endcase
end
// Simple data register (increments on write)
always_ff @(posedge clk) begin
if (rst)
data <= 8'b0;
else if (write && ready)
data <= data + 1;
end
// TODO: Add your assertions here!
endmodule
Then, paste the following SystemVerilog code in testbench.sv.
// Test module with assertions
module tb_fifo_fsm;
logic clk, rst;
logic write, read;
logic valid, ready;
logic [7:0] data;
fifo_fsm dut (
.clk(clk),
.rst(rst),
.write(write),
.read(read),
.valid(valid),
.ready(ready),
.data(data)
);
// Clock generation
initial begin
clk = 0;
forever #5 clk = ~clk;
end
// Test stimulus
initial begin
// Reset
rst = 1;
write = 0;
read = 0;
repeat (2) @(posedge clk);
rst = 0;
// Test sequence: write to partial, attempt write when full, read
repeat (1) @(posedge clk);
write = 1;
repeat (2) @(posedge clk);
write = 0;
repeat (1) @(posedge clk);
read = 1;
repeat (2) @(posedge clk);
read = 0;
repeat (2) @(posedge clk);
$finish;
end
endmodule
On the left sidebar, make sure the following settings are chosen:
- Languages & Libraries
- Testbench + Design: SystemVerilog/Verilog
- UVM/OVM: None
- Other Libraries: None
- Enable TL-Verilog: Not checked
- Enable Easier UVM: Not checked
- Enable VUnit: Not checked
- Tools & Simulators
- Select Synopsys VCS 2023.03
- Open EPWave after run: Not checked
- Show output file after run: Not checked
- Download files after run: Not checked